| VMC home |
| VMC in-vivo |
| VMC in-vivo intercomparisons |
|
EURADOS 2012 head intercomparison |
|---|
The results of the 2012 EURADOS head intercomparison are published in two papers, "EURADOS intercomparison exercise on MC modelling for the in-vivo monitoring of 241Am in skull phantoms Part 1 and Part 2". VMC in-vivo was participant P17 in both Parts. Three different voxel phantoms of the head corresponding to real physical heads were provided for the intercomparison. 241Am in the cranial bone counted using Ge detectors was simulated for the three phantoms. PART 1 the CSR head phantom
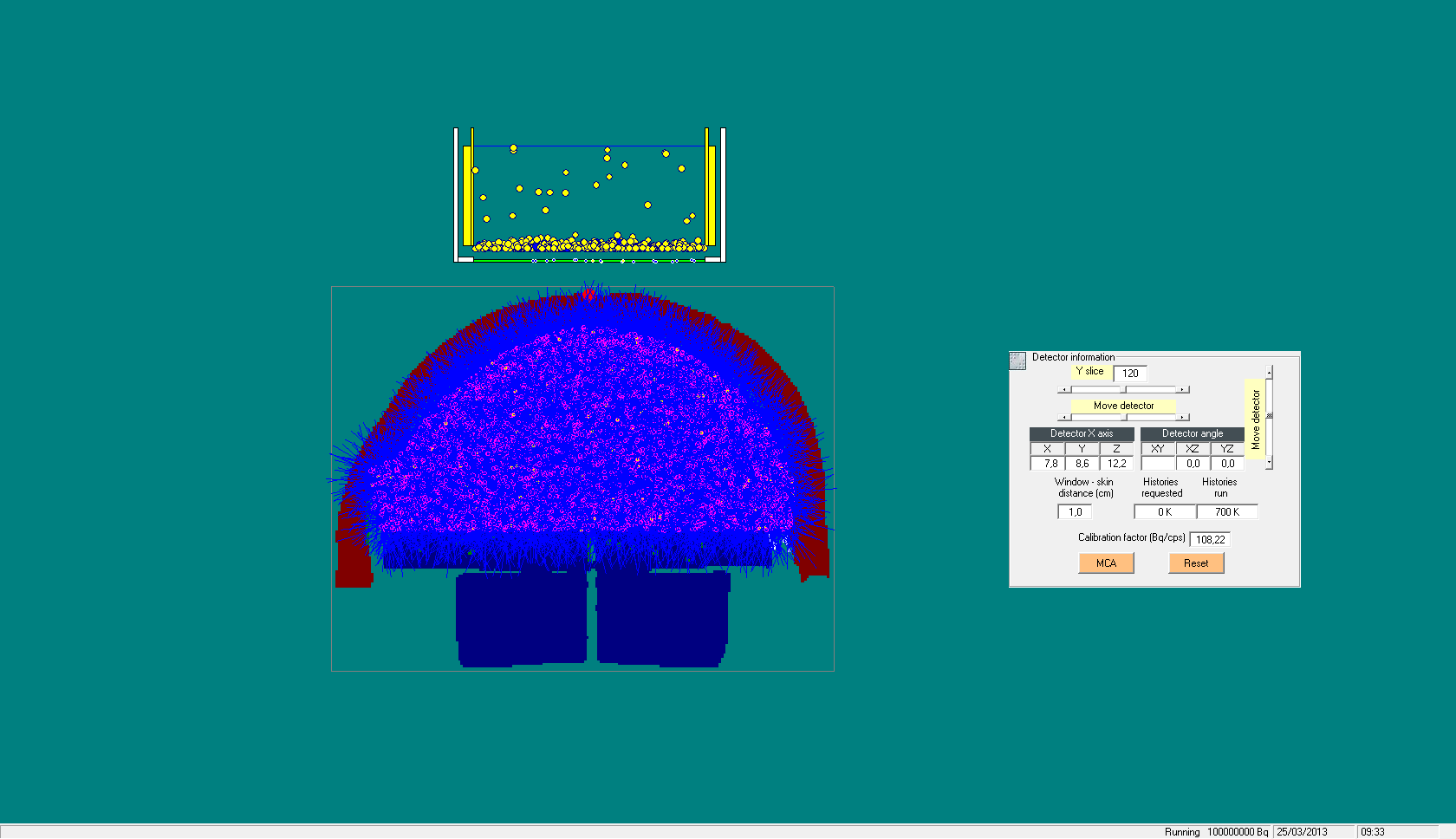
Figure 1 Counting 241Am in the bone of the CSR head phantom with Ge detector.
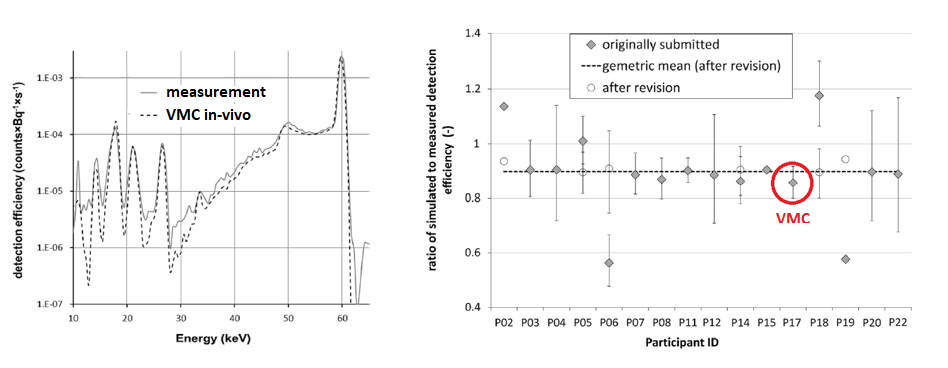
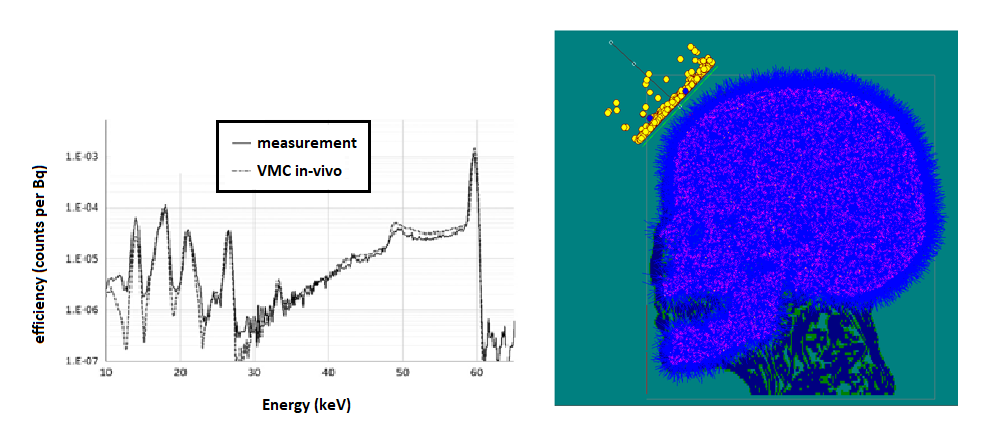
Figure 2. Experimental and VMC in-vivo 241Am spectra and comparison of the participants' relative detection efficiencies with estimated uncertainties for the CSR head intercomparison. PART 2A the CSR head phantom In a similar way as in Part 1, activity of 241Am in the bone of the voxelized CSR head phantom counted using a Ge detector was simulated with VMC in-vivo.
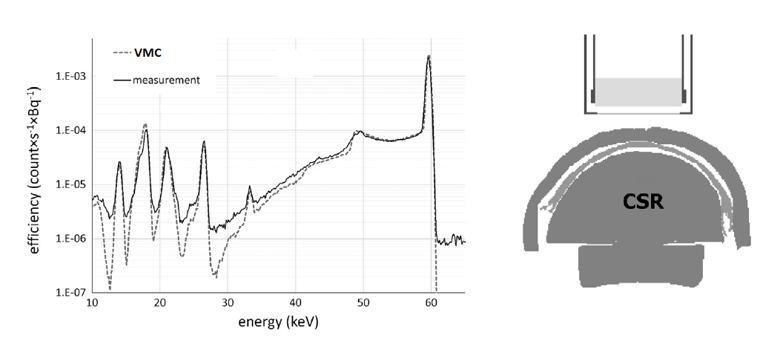
Figure 2. Part 2A - comparison of experimental and VMC results for 241Am in the bone of the CSR head phantom. PART 2B the BPAM-001 head phantom Activity of 241Am in the bone of the voxelized BPAM-001 head phantom counted using a Ge detector was simulated.
Figure 3. Part 2B - experimental measurement and VMC in-vivo simulation comparison for 241Am in the bone of the BPAM-001 phantom and the VMC counting geometry. PART 2C the Bfs head phantom with tilted detector Activity of 241Am in the bone of the voxelized Bfs head phantom counted using a tilted Ge detector was simulated.
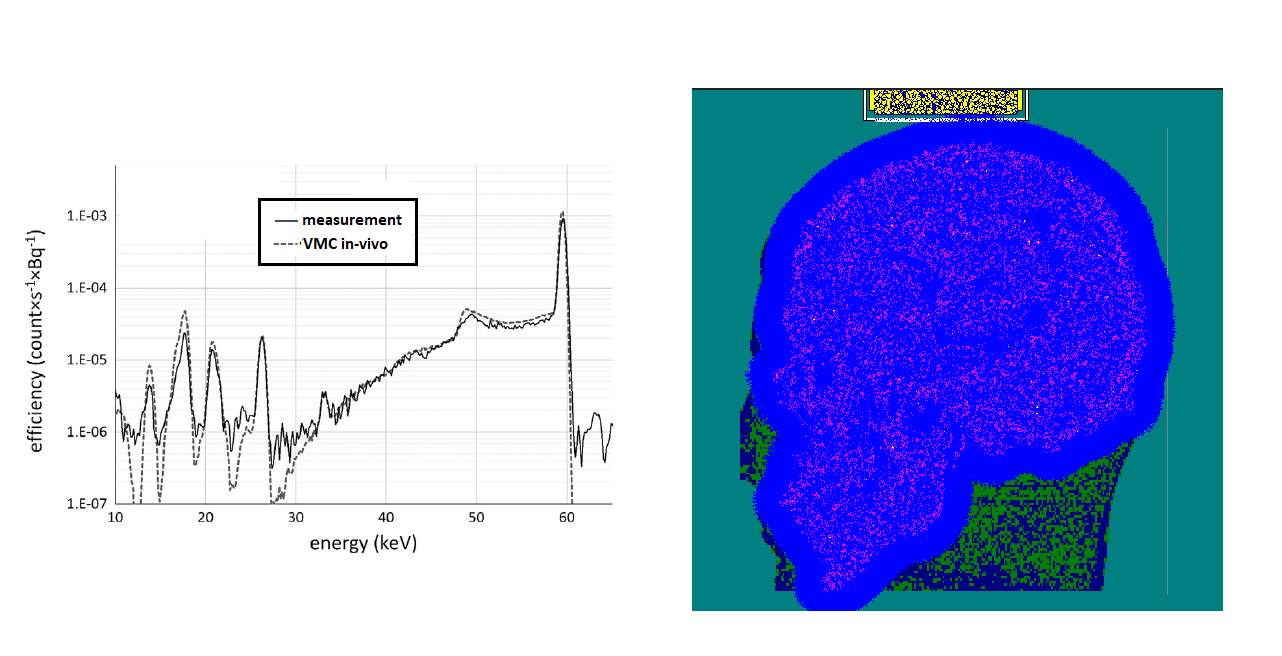
Figure 4. Part 2C - experimental measurement and VMC in-vivo simulation comparison for 241Am in the Bfs phantom and the VMC counting geometry with tilted Ge detector. |